Single-Strand DNA Cuts Trigger Cancer—Mechanism Behind Copy Number Abnormalities Discovered
Press release
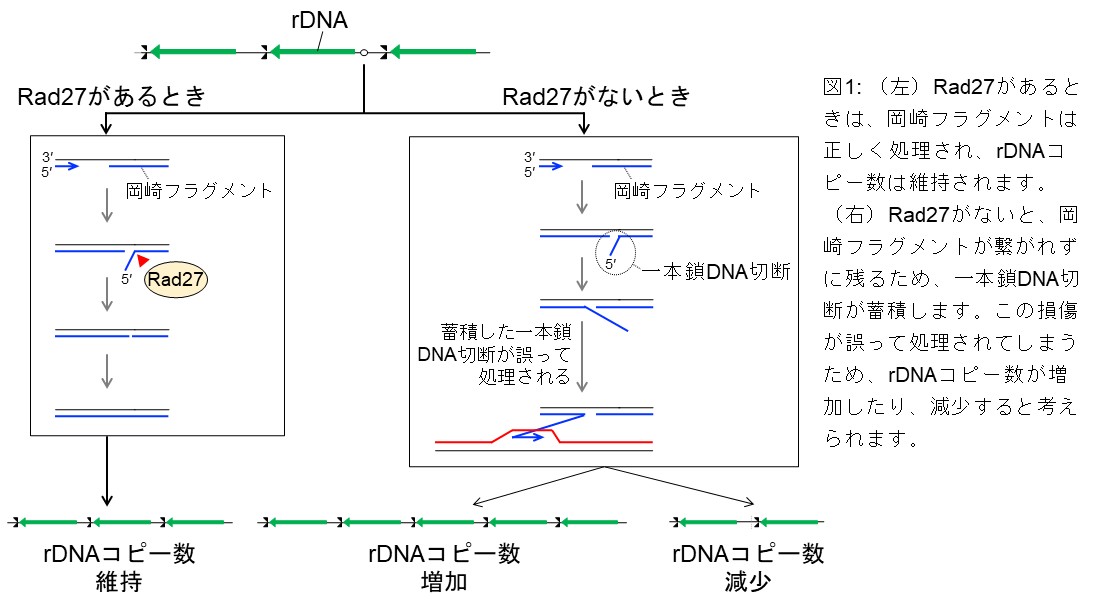
Rad27/FEN1 prevents accumulation of Okazaki fragments and ribosomal DNA copy number changes
Tsugumi Yamaji, Yuko Katayama, Nanase Arata, and Mariko Sasaki
FEBS Letters 2025 DOI:10.1002/1873-3468.70193
![]() Press release (In Japanese only)
Press release (In Japanese only)
DNA copy number changes are the most frequent genomic alterations in cancer cells. Here, we 19 demonstrate that Rad27/FEN-1, a structure-specific nuclease in budding yeast, plays a crucial role in 20 maintaining the stability of the ribosomal DNA (rDNA) repeats. Severe rDNA instability is observed 21 in the rad27∆ mutant, independently of Fob1-mediated DNA replication fork arrest and DNA double-22 strand break (DSB) formation in the rDNA. The rad27Δ mutant accumulates Okazaki fragments in the 23 rDNA region, without inducing formation of detectable DSBs. Similar rDNA instability is observed in 24 DNA ligaseCdc9-deficient cells. Furthermore, Exonuclease 1 and PCNA partially compensate for the 25 loss of Rad27 in the rDNA stabilization. These findings highlight the importance of proper Okazaki 26 fragment maturation in the maintenance of rDNA stability.