Construction of a simple evaluation system for the intestinal absorption of an orally administered medicine using Bombyx mori larvae
Construction of a simple evaluation system for the intestinal absorption of an orally administered medicine using Bombyx mori larvae
Fumika Ichino, Hidemasa Bono, Takeru Nakazato, Atsushi Toyoda, Asao Fujiyama, Kikuo Iwabuchi, Ryoichi Sato, Hiroko Tabunoki
Drug Discoveries & Therapeutics, 12(1) 7-15, 2018 DOI:10.5582/ddt.2018.01004
Human intestinal absorption is estimated using a human colon carcinoma cell line (Caco-2) cells from human colorectal adenocarcinoma, intestinal perfusion, or a mammalian model. These current evaluation systems are limited in their ability to estimate human intestinal absorption. In addition, in vivo evaluation systems using laboratory animals such as mice and rats entail animal ethics problems, and it is difficult to screen compounds on a large scale at the drug discovery stage. Thus, we propose the use of Bombyx mori larvae for evaluation of intestinal absorption of compounds as an alternative system in this study.
Prof. Atsushi Toyoda and Prof. Asao Fujiyama (Center for Information Biology) contributed to sequencing midgut transcriptome of B. mori. Dr. Hidemasa Bono and Dr. Takeru Nakazato (Database Center for Life Science) contributed to this work in comparative analysis of Caco-2 cells, human and B.mori gut transcriptomes.
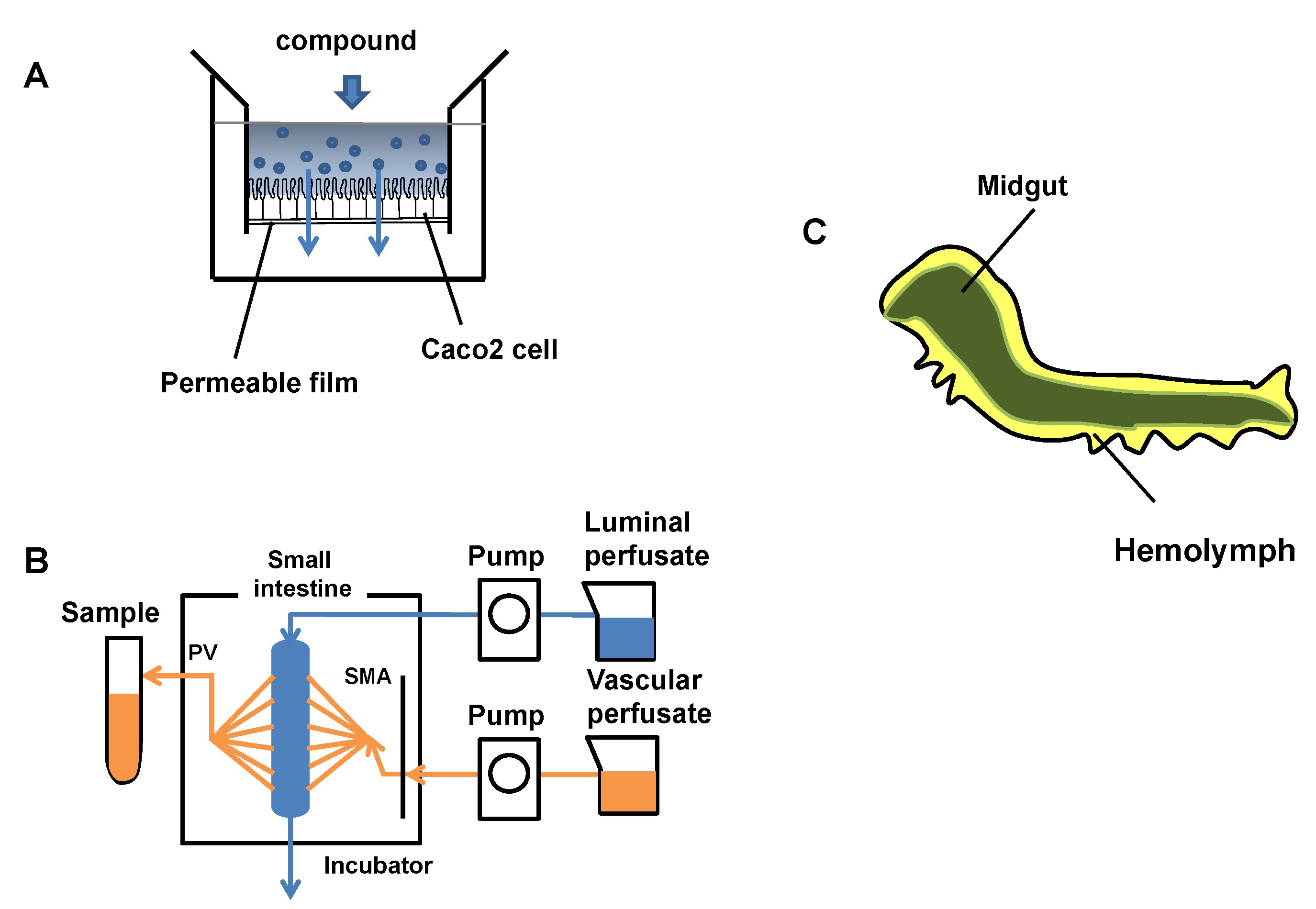
Figure: Evaluation of model systems for intestinal permeability and the internal structure of B.mori larva. Most of the body is occupied by the midgut (green), and its surroundings are filled with hemolymph(yellow).















