Allelic imbalance in regulation of ANRIL through chromatin interaction at 9p21 endometriosis risk locus
Press release
Allelic Imbalance in Regulation of ANRIL through Chromatin Interaction at 9p21 Endometriosis Risk Locus
Hirofumi Nakaoka, Aishwarya Gurumurthy, Takahide Hayano, Somayeh Ahmadloo, Waleed H Omer, Kosuke Yoshihara, Akihito Yamamoto, Keisuke Kurose, Takayuki Enomoto, Shigeo Akira, Kazuyoshi Hosomichi, Ituro Inoue
PLOS Genetics Published: April 7, 2016 DOI:10.1371/journal.pgen.1005893
Press Release (Only in Japanese)
A large number of variants associated with human complex diseases have been discovered by genome-wide association studies (GWASs). These discoveries have been anticipated to be translated into the definitive understanding of disease pathogeneses; however, functional characterization of the disease-associated SNPs remains a formidable challenge. Here we explored regulatory mechanism of a variant on chromosome 9p21 associated with endometriosis, a common gynecological disorder. By scrutinizing linkage disequilibrium structure and DNase I hypersensitive sites across the risk locus, we prioritized rs17761446 as a candidate causal variant. The results of our “allele-specific” functional genomic approaches sheds light on regulatory mechanisms underlying 9p21 endometriosis risk locus, in which preferential bindings of TCF7L2 and its coactivator EP300 to the protective G allele of rs17761446 lead to stronger chromatin interaction with the promoter of ANRIL, which in turn activate transcription of the non-coding RNA. Motivated by the fact that TCF7L2 was a key transcription factor of Wnt signaling pathway, we postulated that the induction of Wnt signaling activated expression levels of ANRIL and cell cycle inhibitors, CDKN2A/2B. Functional genomics on common disease will unlock functional aspect of genotype-phenotype correlations in the post-GWAS stage.
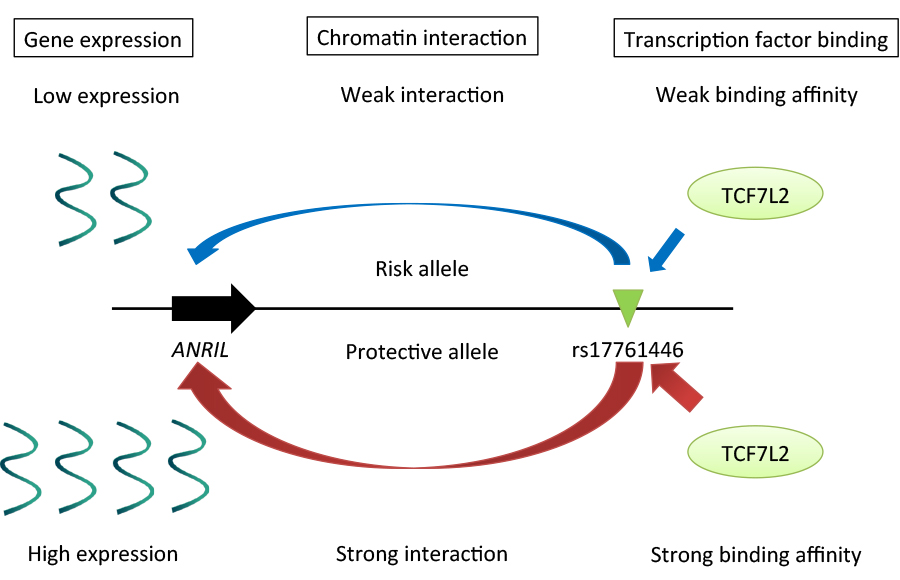
Regulatory mechanisms underlying 9p21 endometriosis risk locus. Preferential bindings of TCF7L2 and its coactivator EP300 to the protective G allele of rs17761446 lead to stronger chromatin interaction with the promoter of ANRIL, which in turn activate transcription of the non-coding RNA.















