A mouse model of human chromosomal disorder, partial trisomy distal 4q
Mammalian Genetics Laboratory・Shiroishi Group
Tamura, M., Hosoya, M., Fujita, M., Iida, T., Amano, T., Maeno, A., Kataoka, T., Otsuka, T., Tanaka, S, Tomizawa, S., and Shiroishi, T.
Human Molecular Genetics, 2013 Jun 15;22(12):2471-2481. DOI: 10.1093/hmg/ddt099
Human chromosomal disorders, such as trisomy or monosomy, occur in over 1% of newborns, and are often associated with developmental failures including congenital heart disease and mental retardation. Though these disorders are likely caused by imbalance in genes involving the trisomic or monosomic region, the molecular bases are unknown in most cases.
In this study, we demonstrated that Recombination-induced mutation 4 (Rim4) is a model animal of human chromosomal disorder, Partial trisomy distal 4q (4q+). Rim4 genome has extra fragment of 6.5Mb from mouse chromosome 8, which is syntenic to the distal end of human Chr4, 4q32.3 to 4q34.1, and contains 17 genes including basic helix-loop-helix transcription (bHLH) factor, Hand2. Rebalancing the gene dosage by genetic cross with Hand2 knockout mouse rescued symptoms of the heart and limb deformities of Rim4. These results suggest that over-dosage of Hand2 causes heart and limb deformities in Rim4 and 4q+, and Rim4 provides a unique animal model to understand the molecular bases underlying the complex phenotypes of 4q+.
This work was carried out in collaboration with National Institute of Genetics (Dr. Shiroishi group) and National Hospital Organization, Niigata Hospital (Dr. Tomizawa group).
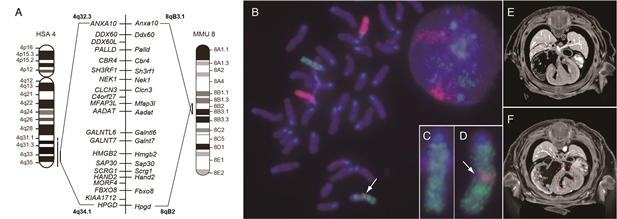
Chromosome aberration and ventricular septal defect observed in Rim4 mutant mouse.
(A) Mouse Chr8 (MMU) 8qB2–B3.1 is syntenic to human Chr4 (HSA4) 4q32.3–34.1, and genes and gene order are well conserved in the syntenic regions of the two species. (B) Dual-color whole chromosome FISH image of Chr6 (green color) and Chr8 (magenta color). Magnified images of Wild type and Rim4/+ Chr6 are shown in insets, (C) and (D), respectively. Arrow in (B) and (D) indicates Chr8-derived insertion fragment. μ-CT images of E14.5 embryos of wild type (E) and Rim4/Rim4 mouse (F) are shown. Dotted circle in (F) indicates ventricular septal defect.















