Saito Group • Invertebrate Genetics Laboratory
Epitranscriptomics in Drosophila
Faculty
▶ Lab HP
Research Summary
RNA acts as not only a carrier of genetic information but also a highly versatile molecule that can be cut, connected, and dramatically change its steric structure. Our laboratory is studying molecular mechanisms and physiological functions of RNA-based gene regulation in Drosophila. To understand them, we are currently engaged in investigating the physiological functions and molecular mechanisms of RNA modifications (epitranscriptome) using biochemical and high-throughput technologies, and genetic tools which are managed and distributed by genetic resources project (NIG-Fly).
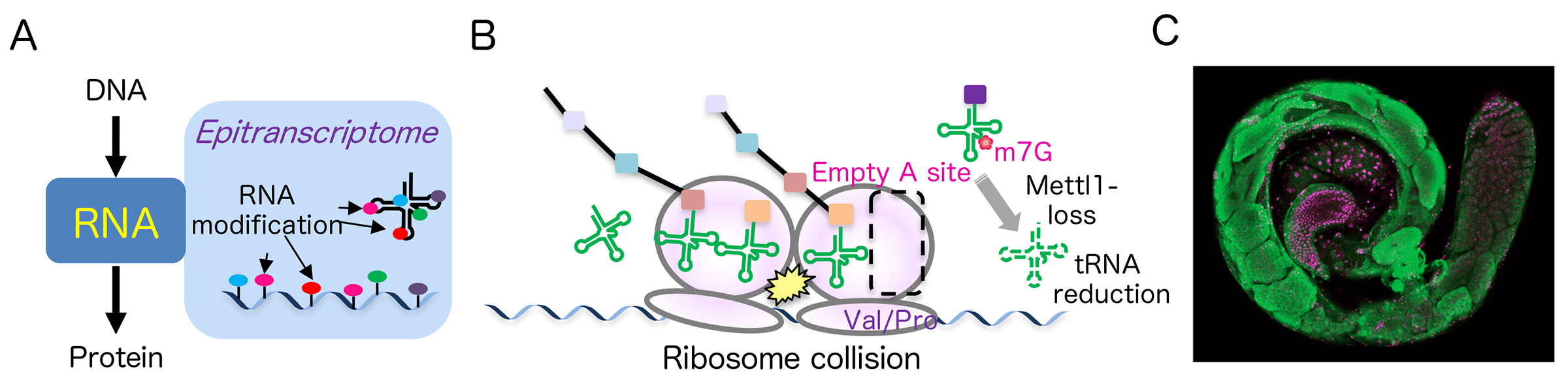
Selected Publications
Kaneko S, Miyoshi K, Tomuro K, Terauchi M, Tanaka R, Kondo S, Tani N, Ishiguro KI, Toyoda A, Kamikouchi A, Noguchi H, Iwasaki S, Saito K. Mettl1-dependent m7G tRNA modification is essential for maintaining spermatogenesis and fertility in Drosophila melanogaster. Nat Commun. 2024 Sep 24;15(1):8147.
Yamamoto-Matsuda H, Miyoshi K, Moritoh M, Yoshitane H, Fukada Y, Saito K, Yamanaka S, Siomi MC. Lint-O cooperates with L(3)mbt in target gene suppression to maintain homeostasis in fly ovary and brain. EMBO Rep. 2022 Oct 6;23(10):e53813.
Utsuno Y, Hamada K, Hamanaka K, Miyoshi K, Tsuchimoto K, Sunada S, Itai T, Sakamoto M, Tsuchida N, Uchiyama Y, Koshimizu E, Fujita A, Miyatake S, Misawa K, Mizuguchi T, Kato Y, Saito K, Ogata K, Matsumoto N. Novel missense variants cause intermediate phenotypes in the phenotypic spectrum of SLC5A6-related disorders. J Hum Genet. 2024 Feb;69(2):69-77.
Takeuchi C, Yokoshi M, Kondo S, Shibuya A, Saito K, Fukaya T, Siomi H, Iwasaki YW. Mod(mdg4) variants repress telomeric retrotransposon HeT-A by blocking subtelomeric enhancers. Nucleic Acids Res. 2022 Nov 11;50(20):11580-11599.

















