Ensuring personal space inside the cell
Kimura Group / Cell Architecture Laboratory
Enucleation of the C. elegans embryo revealed dynein-dependent spacing between microtubule asters
Fujii, K., Kondo, T. & *Kimura
*corresponding author
Life Sci. Alliance (2023) 7, e202302427 DOI:10.26508/lsa.202302427
In psychology, personal space is known as the distance that people tend to maintain from others. A similar phenomenon can be found inside the cell. An organelle called centrosome tend to maintain certain distance from the other centrosomes. In this study, Dr. Ken Fujii and his colleagues investigated the behavior of the centrosomes in enucleated, C. elegans embryonic cells. Using genetics and computational approaches, the researchers proposed that the centrosomes compete with each other for motor proteins “dynein” distributed in the cytoplasm and at the cell cortex to maintain certain distance from the others and ensure their “personal space.” The study has implication in how cellular structures measure distances inside the cell.
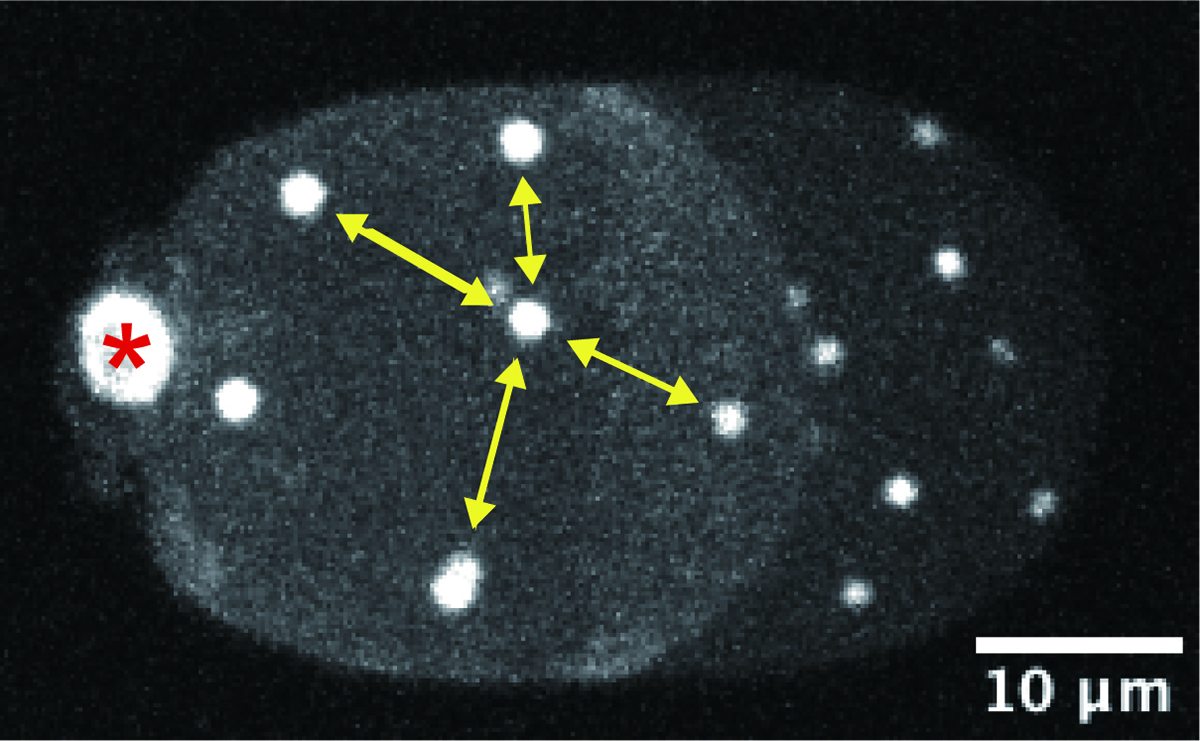
Figure: A representative microscope image of an enucleated, C. elegans embryonic cell. White signals indicate the centrosomes, which are evenly distributed inside the cell. (The image is a 2-dimensional projection of the 3-dimensional cell image. The asterisk indicates the polar body, which is not the centrosome.)















