The ancestor of extant Japanese fancy mice contributed to the mosaic genomes of classical inbred strains.
Press release
The ancestor of extant Japanese fancy mice contributed to the mosaic genomes of classical inbred strains
Takada, T., Ebata, T., Noguchi, H., Keane, K., Adams, D., Narita, T., Shin-I, T., Fujisawa, H., Toyoda, A., Abe, K., Obata, Y., Sakaki, Y., Moriwaki, K., Fujiyama, A., Kohara, Y. and Shiroishi, T.Genome Research, 2013 Aug;23(8):1329-1338. DOI: 10.1101/gr.156497.113
We resequenced the genomes of Mus musculus molossinus-derived two inbred strains, MSM/Ms and JF1/Ms. MSM/Ms originated from Japanese wild mice, and ancestry of JF1/Ms was originally found in Europe and then transferred to Japan. We compared the characteristics of these sequences to those of the C57BL/6J reference sequence and the recent datasets from the resequencing of 17 inbred strains in the Mouse Genome Project.
The major outcomes of this study are summarized below.
1. Over 10 million SNPs and 1 million short indels are identified between the MSM/Ms or JF1/Ms sequence and the B6 reference sequence.
2. In comparison with the B6 reference sequence, the MSM and JF1 sequences contain 38,182 and 38,124 non-synonymous SNPs in 11,489 and 11,313 genes, respectively.
3. Genome introgression from M. m. molossinus into M. m. domesticus is primary framework for the mosaic genomes of classical inbred strains.
4. The genomes of B6 and other classical inbred strains have long consecutive segments with extremely high similarity (>99.998%) to the JF1/Ms strain. This indicates that the ancestor of JF1/Ms was direct origin of M. m. molossinus genome in classical inbred strains.
5. Roughly 30 to 40% of the SNPs detected in pairwise comparisons of classical inbred strains are attributable to the M. m. molossinus genome introgression.
The sequence data of MSM/Ms and JF1/Ms are available through the NIG mouse genome database, with side-by-side comparison to the B6 reference sequence.
This work was carried out in collaboration with National Institute of Genetics (Mammalian Genetics Laboratory, Comparative Genomics Laboratory and Genome Biology Laboratory), RIKEN (BioResource Center and Genome Science Center) and the Wellcome Trust Sanger Institute, and was supported by a Grant-in-Aid for Scientific Research on Priority Areas “Comparative Genomics” and the National BioResource Projects “the Genome Information Upgrading Program” from the Ministry of Education, Culture, Sports, Science and Technology of Japan. This work was also supported in part by the Biodiversity Research Project of the Transdisciplinary Research Integration Center, Research Organization of Information and Systems.
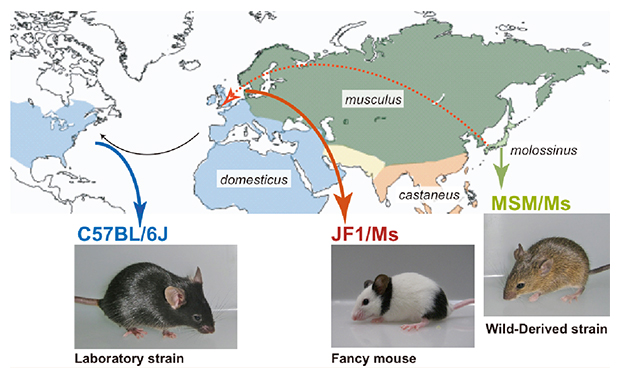
Three mouse strains mainly used in this study. C57BL/6J (B6) is a representative classical inbred strain, which was derived mostly from M. m. domesticus (west European subspecies). MSM/Ms and JF1/Ms originated from M. m. molossinus (Japanese subspecies).















