Why are degron technologies useful for studying nuclear functions?
Ligand-induced degrons for studying nuclear functions
Masato T. Kanemaki
Current Opinion in Cell Biology, advanced online publication (2022) 74, 29–36 DOI:10.1016/j.ceb.2021.12.006
Nuclear functions such as transcription, DNA replication, and DNA repair are closely related to cell proliferation and chromosome segregation. Since cultured cells usually double in about 24 hours, it is crucial to remove the target protein within a few minutes to a few hours to investigate its function in order to avoid secondary effects (Fig. 1). Therefore, the “degron methods”, which enable rapid depletion of a target protein, are ideal for studying nuclear functions.
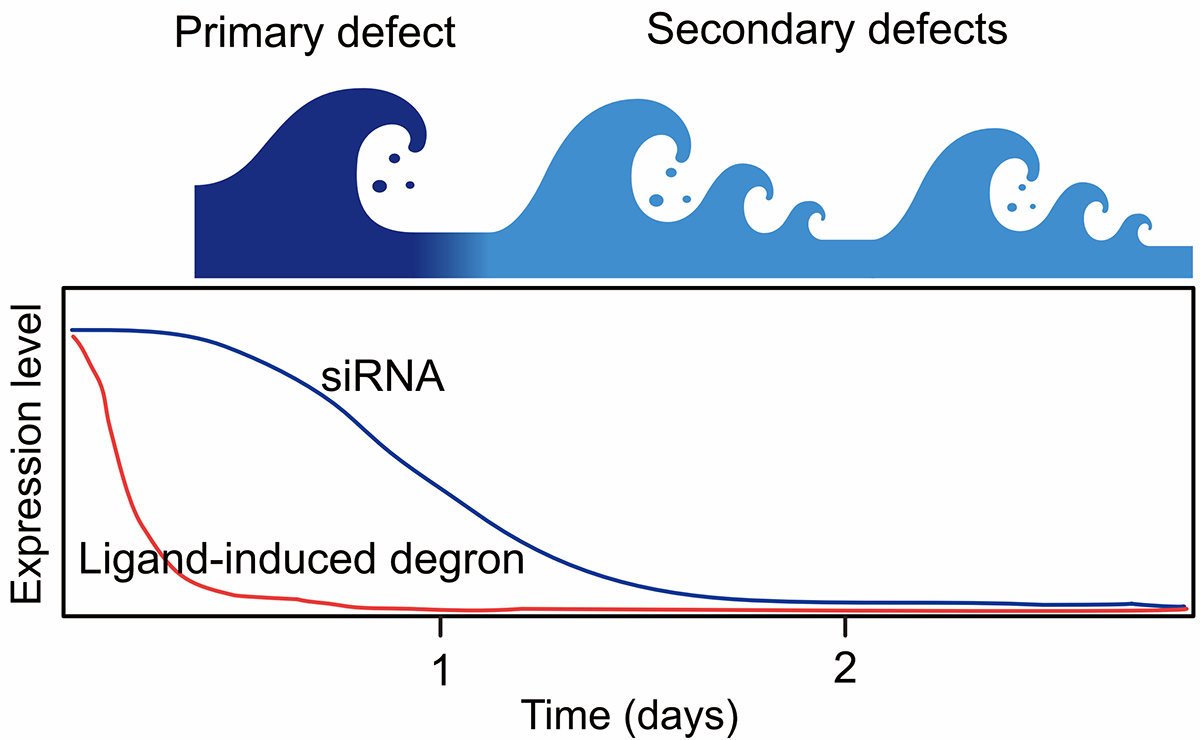
Figure1: Comparison of the effects of target protein when using degron and siRNA methods
In this review article, we described the degron technologies developed so far, including the auxin degron (AID) method developed by our laboratory, and introduced how they have been helpful for research on nuclear functions (Fig. 2). Since degron technologies are relatively new research methods, they are expected to be useful for many studies in the future.
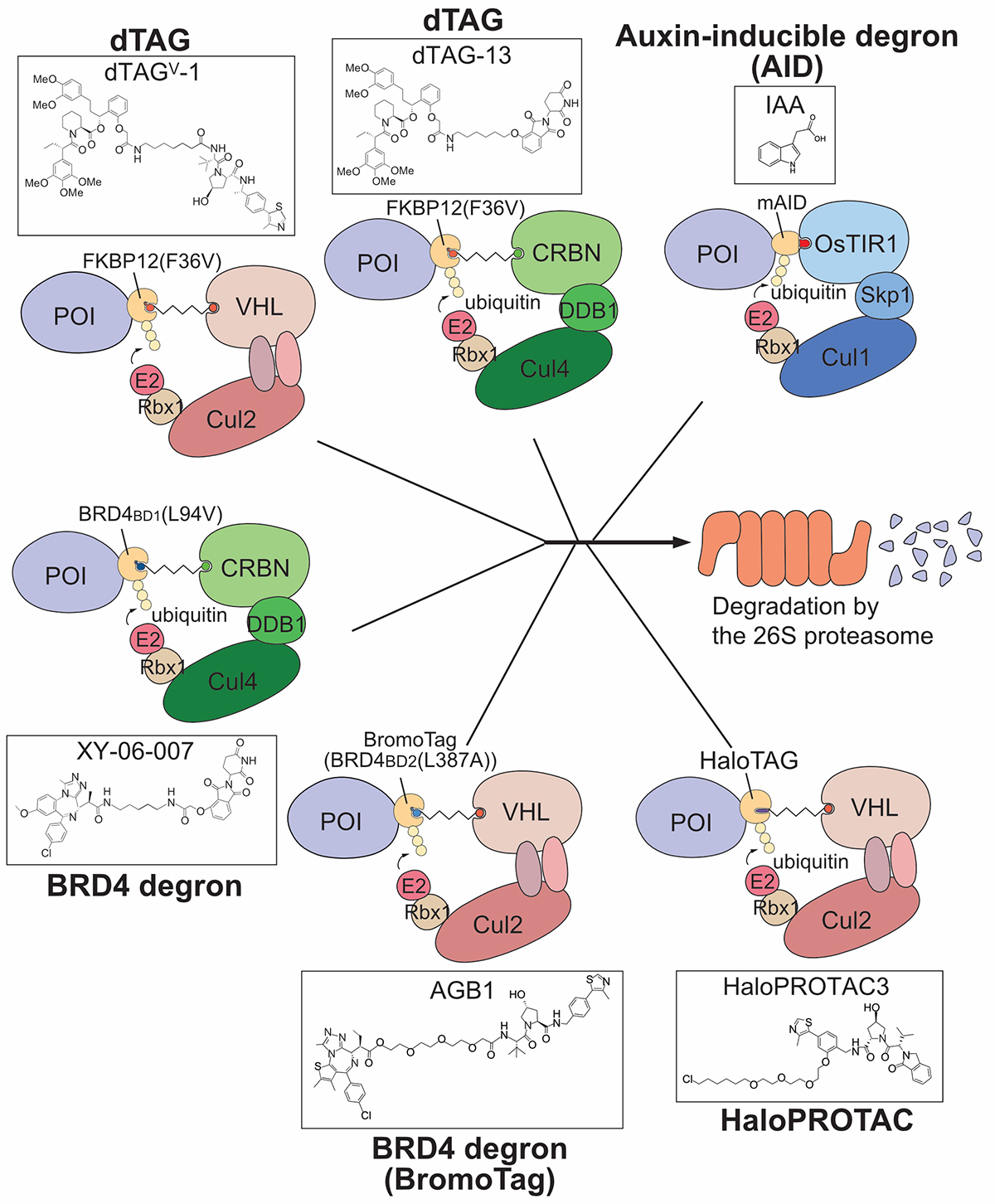
Figure2: The ligand-dependent degron methods developed to date. Except for AID, they are based on a pharmaceutical technology, PROTAC.
This paper will be published in the “Cell Nucleus” issue (June, 2022) in Current Opinion in Cell Biology, edited by Prof. Kazuhiro Maeshima at National Institute of Genetics and Prof. Eran Meshorer at the Hebrew University of Jerusalem.















