Rtt109 Prevents Hyper-Amplification of Ribosomal RNA Genes through Histone Modification in Budding Yeast
Division of Cytogenetics・Kobayashi Group
Satoru Ide, Kimiko Saka, and Takehiko Kobayashi
PLOS Genetics, 2013 Apr;9(4):e1003410. DOI: 10.1371/journal.pgen.1003410
Gene amplification is one of the major strategies used by cells to increase the abundance of gene products. We have been studying amplification of the rDNA cluster in yeast with a focus on distinguishing the contributions of unequal sister-chromatid recombination vs rolling circle-type amplification as observed in the early developmental stage in amphibian oogenesis. It is not known how these two modes of amplification switch. We screened for yeast mutants in which rDNA copy number was unstable and found and characterized an rtt109 mutant that has an abnormally high rDNA copy number. Evidence is presented that the rolling circle-type amplification occurs in this mutant. Therefore, RTT109 plays a key role in regulating mode of rDNA amplification.
Variation in gene copy number (amplification) has been widely detected in various organisms, contributing to both beneficial adaptation and pathology (e.g., cancer). Our results shed new light on molecular mechanisms of gene amplification.
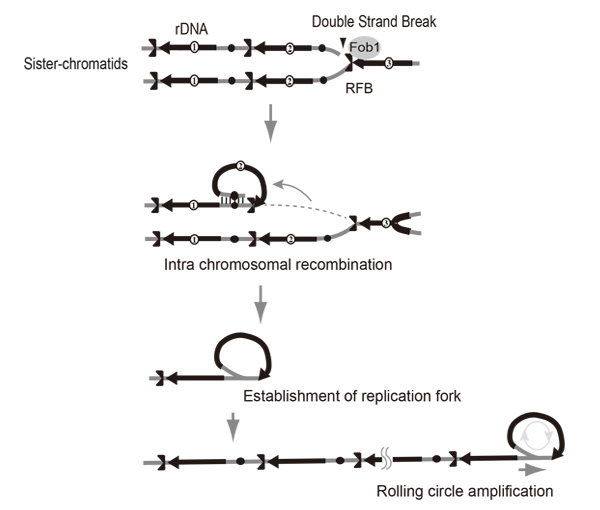
Rolling circle replication by intra-sister chromatid recombination.The broken end at the RFB (Replication Fork Barrier site) recombines via intra-sister chromatid exchange followed by rolling circle replication.















